Docker
Overview Copied
Docker monitoring is a Gateway configuration file that enables monitoring of Docker installations through a set of samplers with customised Toolkit plug-in settings.
This can be monitored locally or remotely. If you set up the Docker installation locally, the Docker daemon and Netprobe will run on the same machine. If you want to monitor it remotely, then the Docker daemon Netprobe will not run on the same machine.
Track the following key areas when using Docker monitoring:
| Key Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Status | Provides information about the containers running on the host, including their container ID, name, port information, and size. |
| Usage | Collects performance statistics about each container and returns each container’s individual CPU and Memory utilisation information, Net IO, Block IO Information, and the configured limits. |
Intended audience Copied
This guide is intended for users who are setting up, configuring, troubleshooting and maintaining this integration. This is also intended for users who will be using Active Console to monitor data from Docker. Once the integration is set up, the samplers providing the dataviews become available to that Gateway.
As a user, you should be familiar with Python or any other database, and with the administration of the Docker services.
Prerequisites Copied
The following requirements must be met before the installation and setup of the template:
- A machine running the Netprobe must have access to the host where the Docker instance is installed and the port Docker is listening to.
- Netprobe 4.6 or higher.
- Gateway 4.8 or higher.
- Python 2.7 or higher.
- Docker 17.12.0-ce.
- CentOS 7.
Installation procedure Copied
Ensure that you have read and can follow the system requirements prior to installation and setup of this integration template.
-
Download the integration package
geneos-integration-docker-<version>.zipfrom the ITRS Downloads site. -
Open Gateway Setup Editor.
-
In the Navigation panel, click Includes to create a new file.
-
Enter the location of the file to include in the Location field. In this example, it is the
include/DockerMonitoring.xml. -
Update the Priority field. This can be any value except
1. If you input a priority of1, the Gateway Setup Editor returns an error. -
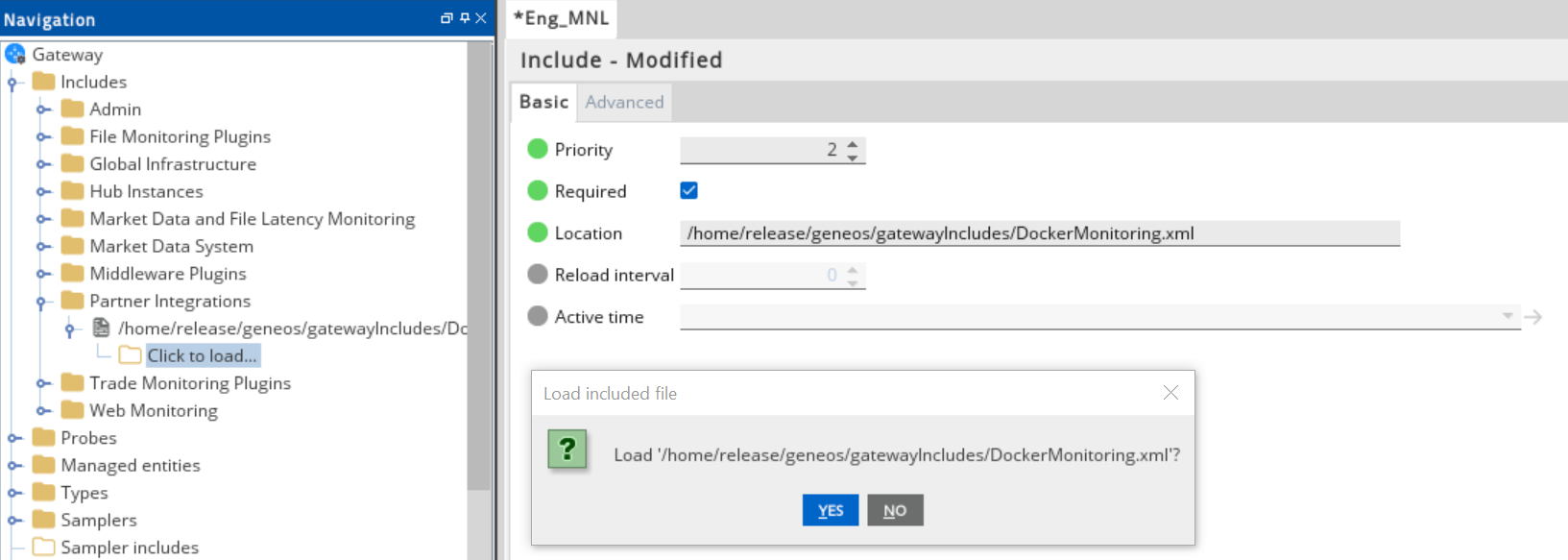
Expand the file location in the Include section.
-
Select Click to load.
-
Click Yes to load the new Docker include file.
-
Click Managed entities in the Navigation panel.
-
Add the Docker type to the Managed Entity section that you will use to monitor Docker.
-
Click Validate current document
 to check your configuration.
to check your configuration. -
Click Save current document
 to apply the changes.
to apply the changes.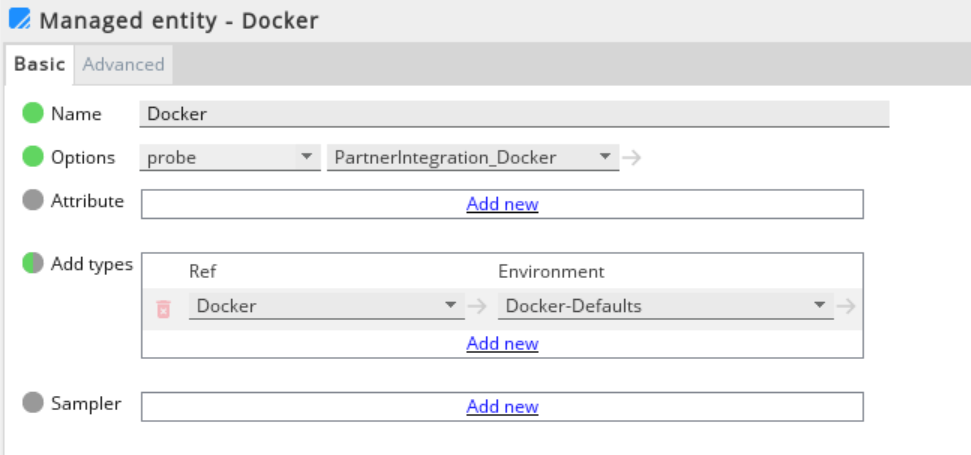
Set up the samplers Copied
These are the pre-configured samplers available to use in DockerMonitoring.xml.
Configure the required fields by referring to the table below:
| Samplers |
|---|
| Docker-Usage |
| Docker-Status |
Set up the variables Copied
The DockerMonitoring.xml template provides the following variables that are set in the Environments section.
For locally installed Docker, where the Docker daemon and Netprobe are running on the same machine:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| DOCKER_PYTHON_EXE | Fully qualified path to python executable. Default: /usr/bin/python. |
| DOCKER_HOST | IP/Hostname of the server where Docker daemon is running. Mandatory: No |
| DOCKER_PORT | Port where the Docker daemon is waiting for connections. Mandatory: No |
| DOCKER_TLS_CA_CERT | Refers to <path-to-file>/ca.pem Mandatory: No |
| DOCKER_TLS_CERT | Refers to <path-to-file>/cert.pem Mandatory: No |
| DOCKER_TLS_KEY | Refers to <path-to-file>/key.pem Mandatory: No |
For remotely installed Docker, where the Docker daemon and Netprobe are not running on the same machine:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| DOCKER_PYTHON_EXE | Fully qualified path to python executable. Default: /usr/bin/python |
| DOCKER_HOST | IP/Hostname of the server where Docker daemon is running. |
| DOCKER_PORT | Port where the Docker daemon is waiting for connections. |
| DOCKER_TLS_CA_CERT | Refers to <path-to-file>/ca.pem Mandatory: Yes |
| DOCKER_TLS_CERT | Refers to <path-to-file>/cert.pem Mandatory: Yes |
| DOCKER_TLS_KEY | Refers to <path-to-file>/key.pem Mandatory: Yes |
| DOCKER_TLS_AUTHENTICATION | Flag whether TLS authentication should be used. Default: True |
Note
In this set-up, TLS authentication is required to be configured in the Docker daemon. The ca, cert, and key .pem files are generated separately using OpenSSL.
Set up the rules Copied
The DockerMonitoring-SampleRules.xml template also provides a separate sample rules that you can use to configure the Gateway Setup Editor.
Your configuration rules must be set in the Includes section. In the Navigation panel, click Rules.
The table below shows the included rule setup in the configuration file:
| Rules | Sample Rules |
|---|---|
| Docker-Usage | cpuPercentUsage-High |
| memPercentUsage-High | |
| Docker Status | size-High |
Metrics and dataviews Copied
Docker status Copied

| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| containerName | Unique container name user assigned or automatically assigned by Docker daemon. |
| containerId | Unique container ID that corresponds to the container name. |
| image | Image name/ID from which the container is based on. |
| status | Container status/active age.
Unit: days |
| ports | Exposed ports including external mapping if available. |
| size | Container disk size which is a writable memory layer.
Unit: megabytes (MB) |
| virtualSize | Container disk size which image shared memory layer is shared by all containers based on the same image. Unit: megabytes (MB) |
Docker usage Copied

| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| containerName | Unique container name user assigned or automatically assigned by Docker daemon. |
| containerId | Unique container ID that corresponds to the container name. |
| cpuPercentUsage | CPU utilisation expressed in percentage(%). |
| memUsage | Current memory utilisation. Unit: megabytes (MB) |
| memLimit | Memory utilisation limit for the container. |
| memPercentUsage | Memory utilisation expressed in percentage (%) |
| NetInput | Network IO usage. Unit: megabytes (MB) |
| NetOutput | Network IO limit. Unit: megabytes (MB) |
| blockInput | Disk IO usage. Unit: megabytes (MB) |
| blockOutput | Disk IO limit. Unit: megabytes (MB) |
| pids | Number of PIDs (Not available on Windows). |