Clusters
A cluster is a logical collection of servers and storage that allow sharing of resources for a common collection of virtual machines while ensuring high availability and load balancing. In the default Baseline View, clusters are displayed as one of the default active groupings in the sunburst.
The Clusters panel provides a summary of all clusters visible in the current active Baseline View . It shows the number of redundant hosts in a cluster, as well as the number of reference workloads that can be added to this cluster before the redundancy policy is breached or before the cluster reaches full saturation.
Display cluster details Copied
Details about clusters, such as headroom or high availability policies, can be accessed from the Clusters panel located to the right of the sunburst. The panel displays the list of all clusters currently visible in the sunburst.
Click Options ![]() of the cluster to see additional actions:
of the cluster to see additional actions:
- Headroom — displays all headroom details for the selected cluster.
- Alternatively, you can right-click a cluster directly in the sunburst, and then select Headroom to see the details. For more information, see Headroom.
- Go to — immediately zooms into the selected cluster and displays details only for this cluster.
- Locate — highlights the cluster in the sunburst.
Cluster high availability (HA) policies Copied
In your IT infrastructure, you may want to ensure that a number of devices within a cluster are redundant. This means that if these devices fail, there is still capacity in a cluster to ensure continued operation of the machines in that cluster.
Redundancy is normally expressed in the form of N+x, where x is the number of backup components required.
In the case of virtualisation clusters, N is the number of devices needed to support the demand within the cluster adequately, and x refers to the number of additional hosts. Therefore, when a cluster has a high availability policy of N+2, it can withstand the failure of 2 hosts and still have sufficient capacity to support the aggregate workload of all the virtual machines in that cluster.
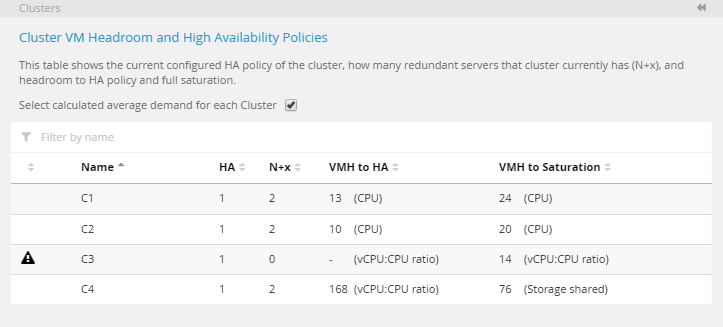
The Clusters panel displays a table that shows the following information and calculations for each cluster that is currently visible in the sunburst:
- Policy breach warning
 — the first column in the list is used to indicate if a cluster is in breach of HA policy. If it is, a warning icon is displayed.
— the first column in the list is used to indicate if a cluster is in breach of HA policy. If it is, a warning icon is displayed. - HA — the current configured high availability policy of each cluster. A value of
1indicates that the cluster is expected to have a HA policy of N+1, which means that there must be at least one redundant server. - N+x — the highest level of redundancy currently achievable for that cluster given the baseline resource utilisation profile. If there are 3 or more redundant servers in the cluster, the value will be presented as
3+.
The is default value is set to1and can be changed by contacting your account representative. - VMH to HA — the number of reference workloads that can be added to this cluster before the redundancy policy is breached. This is based on the selected calculation metrics configured using the VM headroom panel. For more information, see Headroom.
- VMH to saturation — the number of reference workloads that can be added to this cluster before reaching full saturation. By default, saturation is considered to be full capacity minus the operational reserve. For CPU, the default reserve is 20% and for active memory it is 40%.
Calculate average demand for cluster Copied
By default, the cluster headroom table uses the global headroom reference to determine redundancy, headroom to N+x capacity, and full capacity. However, some clusters may have workloads that deviate significantly from the average (for example, a cluster of SQL server machines). In this case using a global average machine as a reference may overstate capacity for that cluster.
For more information about how reference is calculated, see Reference workload.
You can choose to use a calculated average per cluster. To do this, follow these steps:
- In the Clusters panel, select the Select calculated average demand for each Cluster check box.
- Click Apply changes. The button appears when you make changes in the panel.
After a brief calculation, the table updates to show headroom and redundancy figures using a calculated average per cluster.
Changing the calculations from the global reference to average demand for cluster results in the headroom figure that is displayed in the Clusters panel to be different from the headroom figure in the sunburst. To make these numbers appear in a consistent way, follow these steps:
- Right-click a cluster in the sunburst.
- From the dialog box, select Workloads and then Calculate average.
- Select the Set this template as the reference used for headroom calculations check box.
The numbers for the chosen cluster now match.
Example Copied
The image below shows the cluster table using global headroom reference:
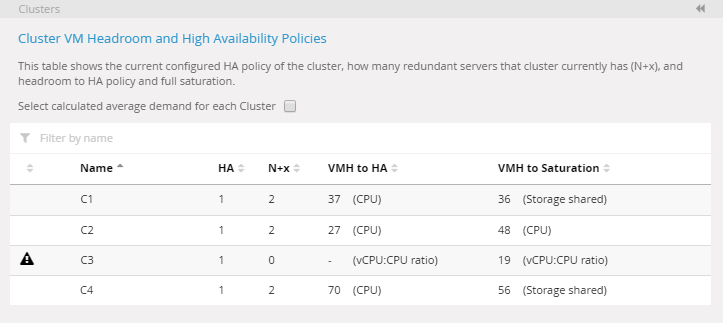
Cluster table using calculated average per cluster. The headroom figures have changed accordingly.